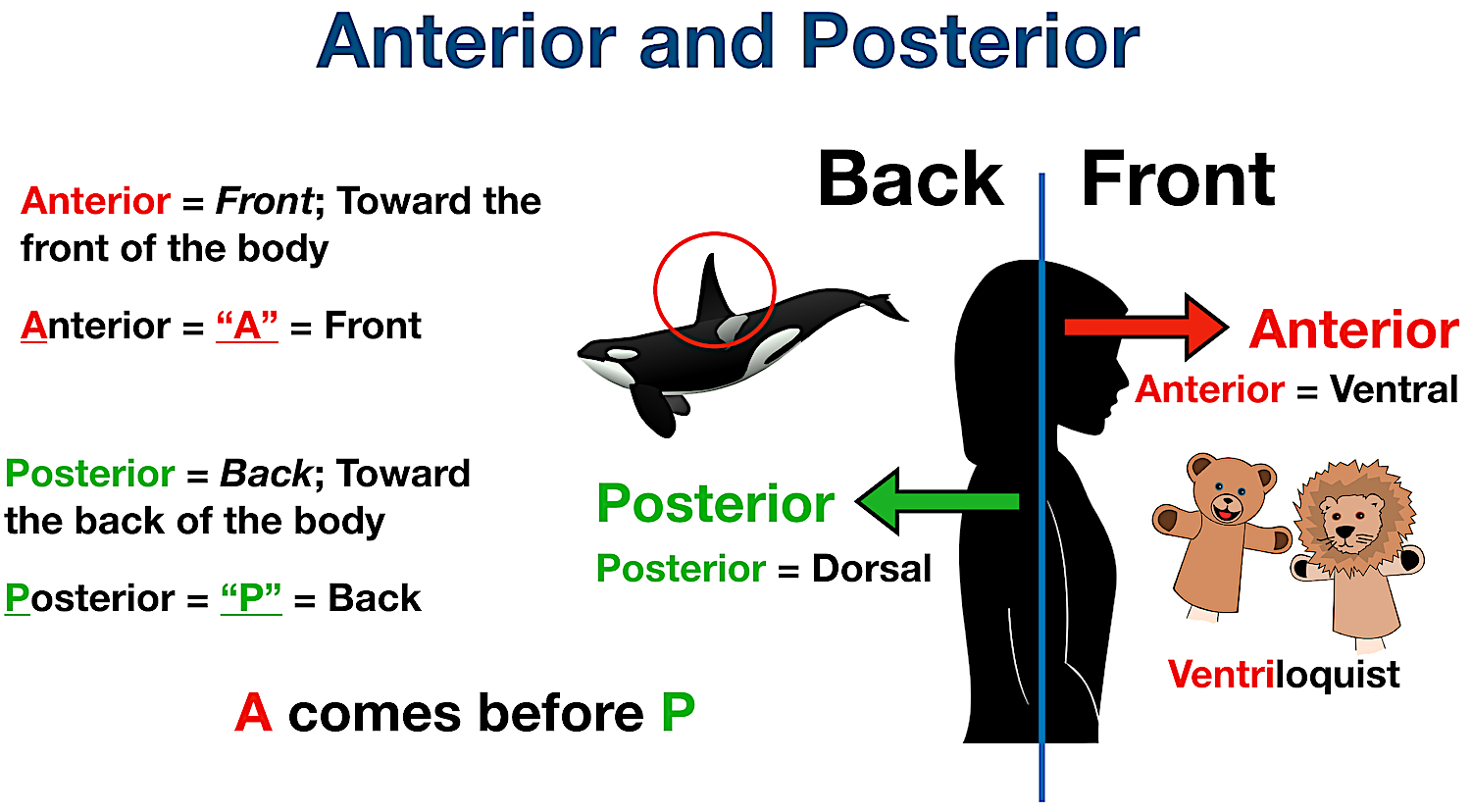
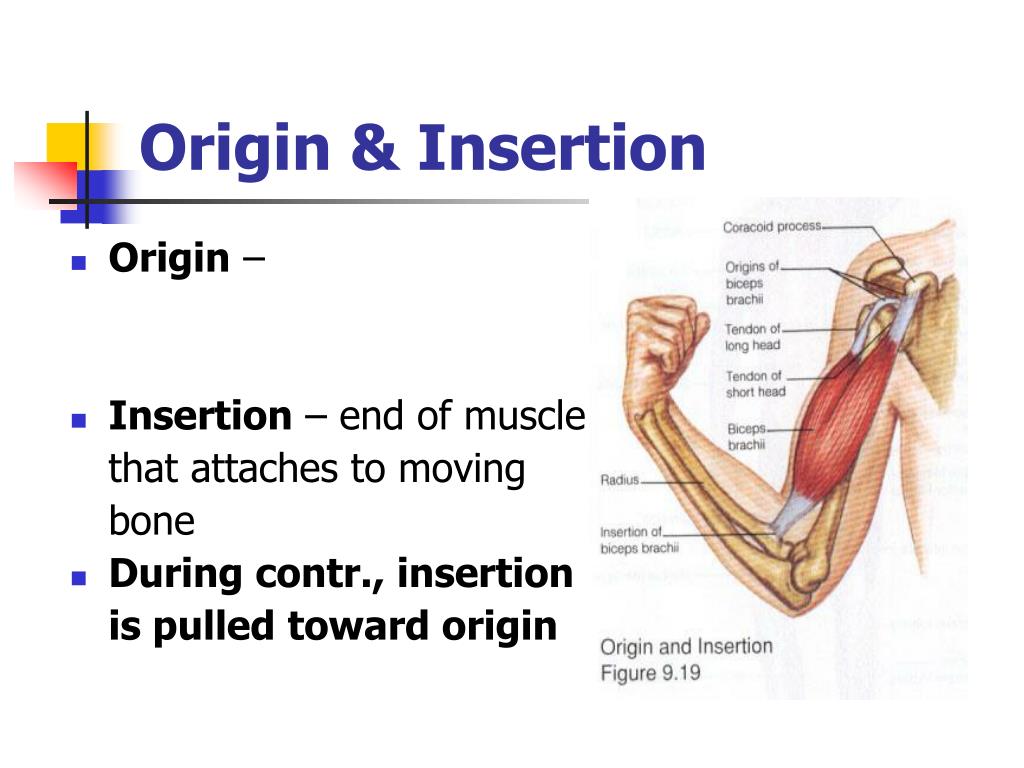
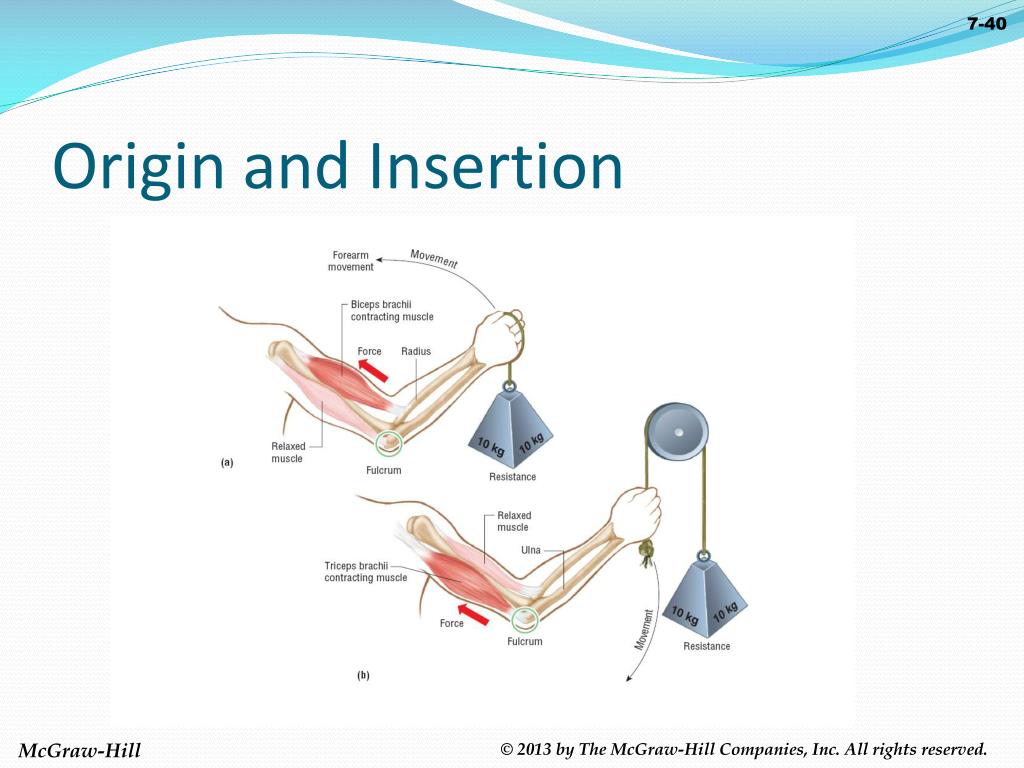
What Does Insertion Mean In Anatomy - The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. It is usually located distal to the. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles.
The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. It is usually located distal to the. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts.
It is usually located distal to the. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. It is usually located distal to the. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. The origin.
PPT The Muscular System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. It is usually located distal to the. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to.
Trapezius Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action vrogue.co
It is usually located distal to the. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to.
What Is A Insertion Point
The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. It is usually located distal to the. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin,.
Insertion of Tibialis Anterior Muscle Complete Anatomy
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. It is usually located distal to the. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. It is usually located distal to the. The origin.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. It is usually located distal to the. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin,.
Insertion Anatomy Definition Anatomy Drawing Diagram Muscle
The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. It is usually located distal to the. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin,.
In The World Of Anatomy, Origin And Insertion Are Crucial When Discussing Muscles.
The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. It is usually located distal to the.